Each of the 6 topics has a specific number of tasks, hierarchically arranged according to difficulty levels. The topics were structured along progressively increasing difficulty levels, moving from easier tasks to increasingly difficult ones. At each difficulty level, several versions of each question type are produced. In case the student successfully solves the problem, he/she can move up to a higher level, if he/she fails, he/she will fall back to an easier level, in which case he/she will be given a different problem from the ones in the level.
Some topics was processed using two learning modules, a linear and an adaptive pathway. In total, there are 6 linear and 6 adaptive modules.
- linear route: an "information" MODULE
- adaptive pathway: a "skills gap filling" MODULE
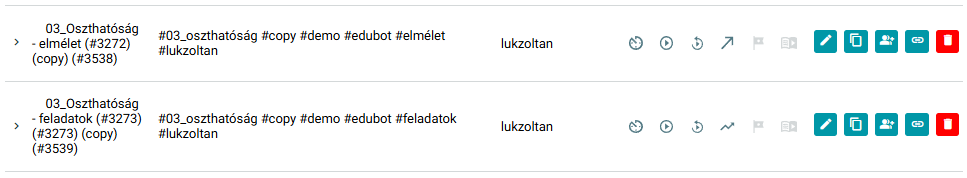
Linear pathway: consists of theoretical knowledge elements, summarising what knowledge the student should have for the given topic. The linear pathway aims to ensure that the student masters/repeats the basics of the topic, such as definitions, basic concepts, formulas, etc.
Demonstrating the structure of linear content within the topic of Divisibility
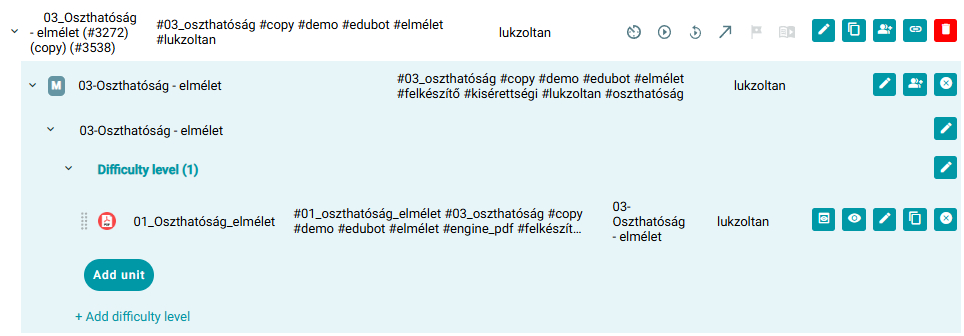
Adaptive route:
Content of the adaptive pathway: increasingly difficult practice exercises with help tasks and explanations
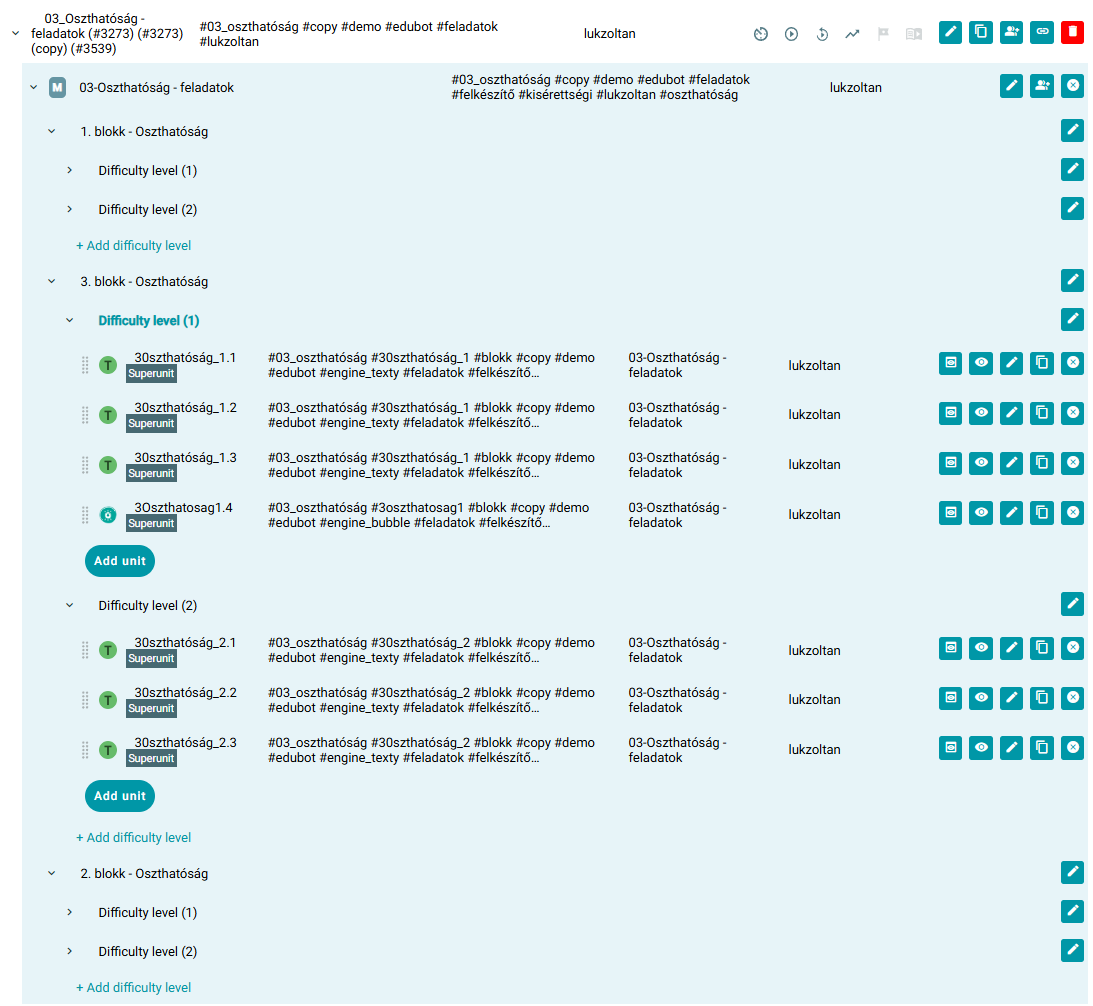
- adaptive modules each contain at least three blocks, with increasingly difficult tasks in line with the skills assessment test methodology.
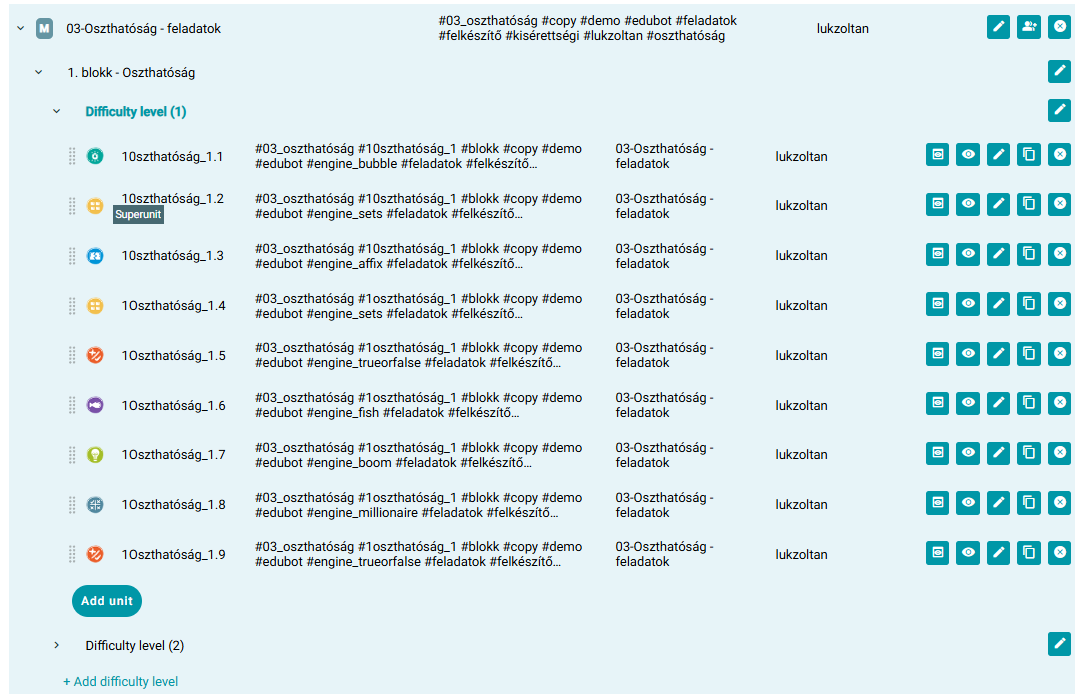
- Block 1 contains easier tasks, with occasional help elements
- Block 2 contains tasks of medium difficulty
- Block 3 contains more difficult, competition-level tasks
- the difficulty levels contain at least two sub-levels of 3-5 superunits
- content of the superunits: main task - supporting task/knowledge element - text or video explanation, if appropriate. The knowledge element with a facilitating function conveys some theoretical knowledge in a textual form, while the facilitating task is an interactive, game based exercise.
Demonstrating the structure of adaptive content within the theme of Divisibility
Block 1: easier tasks, occasional superunits.
Block 2: contains exercises of medium difficulty to help strudents prepare for the more difficult tasks. This block contains 2 levels, with several superunit tasks per level, which include a help task/knowledge element and an explanation in addition to the main task.
Block 2 of each topic contains 10-20 super-units, each of which contains an interactive main task, knowledge element and/or supporting task, with an explanation depending on the complexity of the task.

Block 3: only more difficult tasks, corresponding to the third and final level of the aptitude test. At this level, each main task is accompanied by at least one knowledge element, text or video explanation.
Illustration of the structure of the examination papers within the topic of Divisibility
